GOMOS
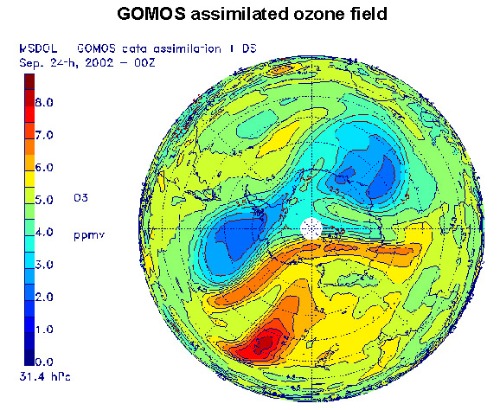
The Global Ozone Monitoring by Occultation of Stars (GOMOS) instrument was an atmospheric sensor on board the Envisat satellite, operational from 2 March 2002 to 8 April 2012. GOMOS was an ESA funded instrument and developed as a joint project of Finland and France. It contributed, together with SCIAMACHY and MIPAS, to atmospheric sounding and the monitoring of ozone with high accuracy.
The main scientific objective of this stellar occultation instrument was to monitor ozone and ozone trends in the stratosphere and mesosphere with high accuracy and high vertical resolution at global coverage. Moreover, GOMOS enabled measuring atmospheric parameters related to stratospheric ozone chemistry like NO2, NO3, H2O and aerosol as well as ozone dynamics like temperature, air density and turbulence. These tasks were achieved by measuring stellar spectra in the ultraviolet to near infrared range while stars are being eclipsed by Earth. It was regarded as a demonstrator for the stellar occultation technique and a precursor for other occultation instruments.