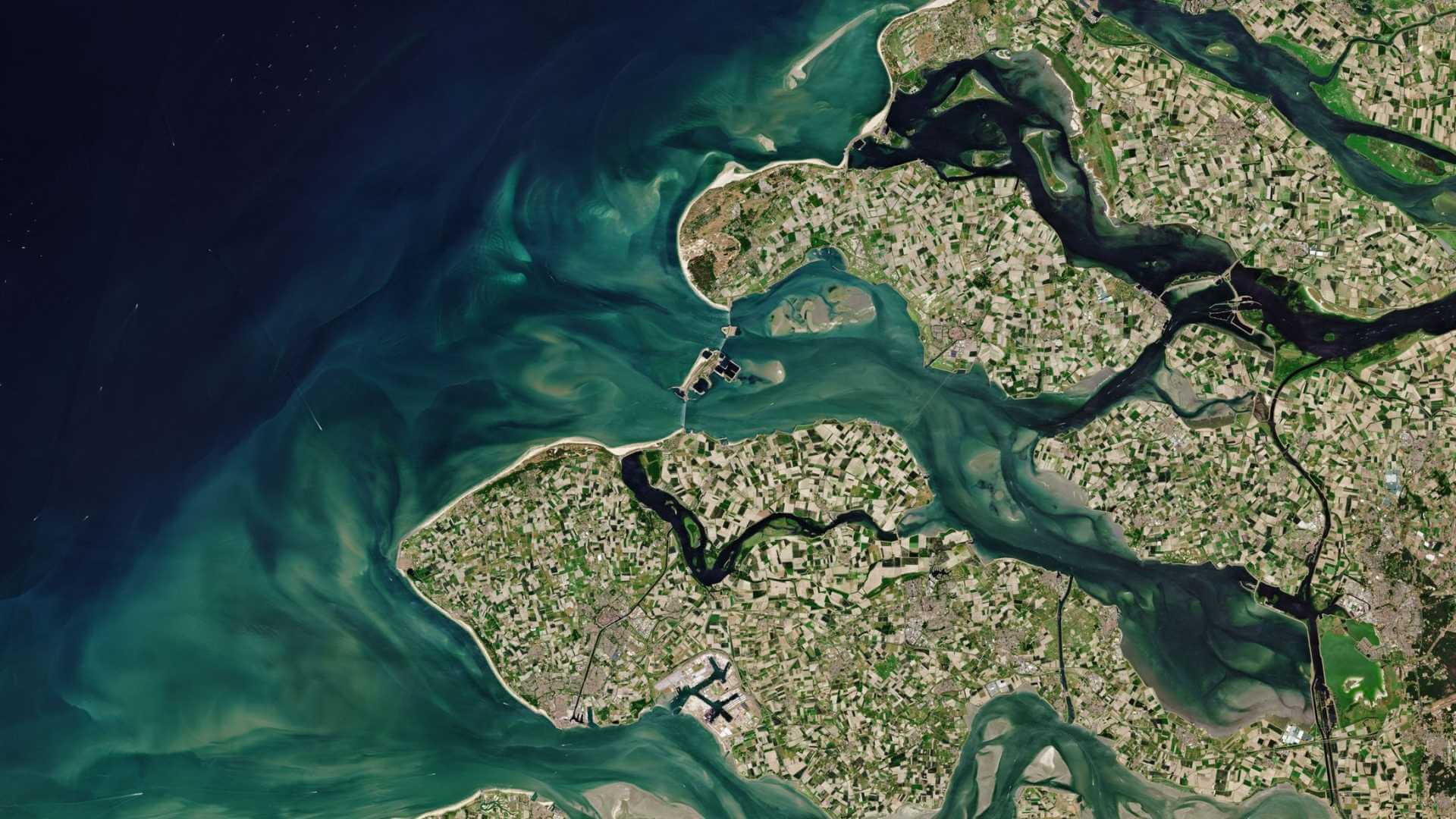
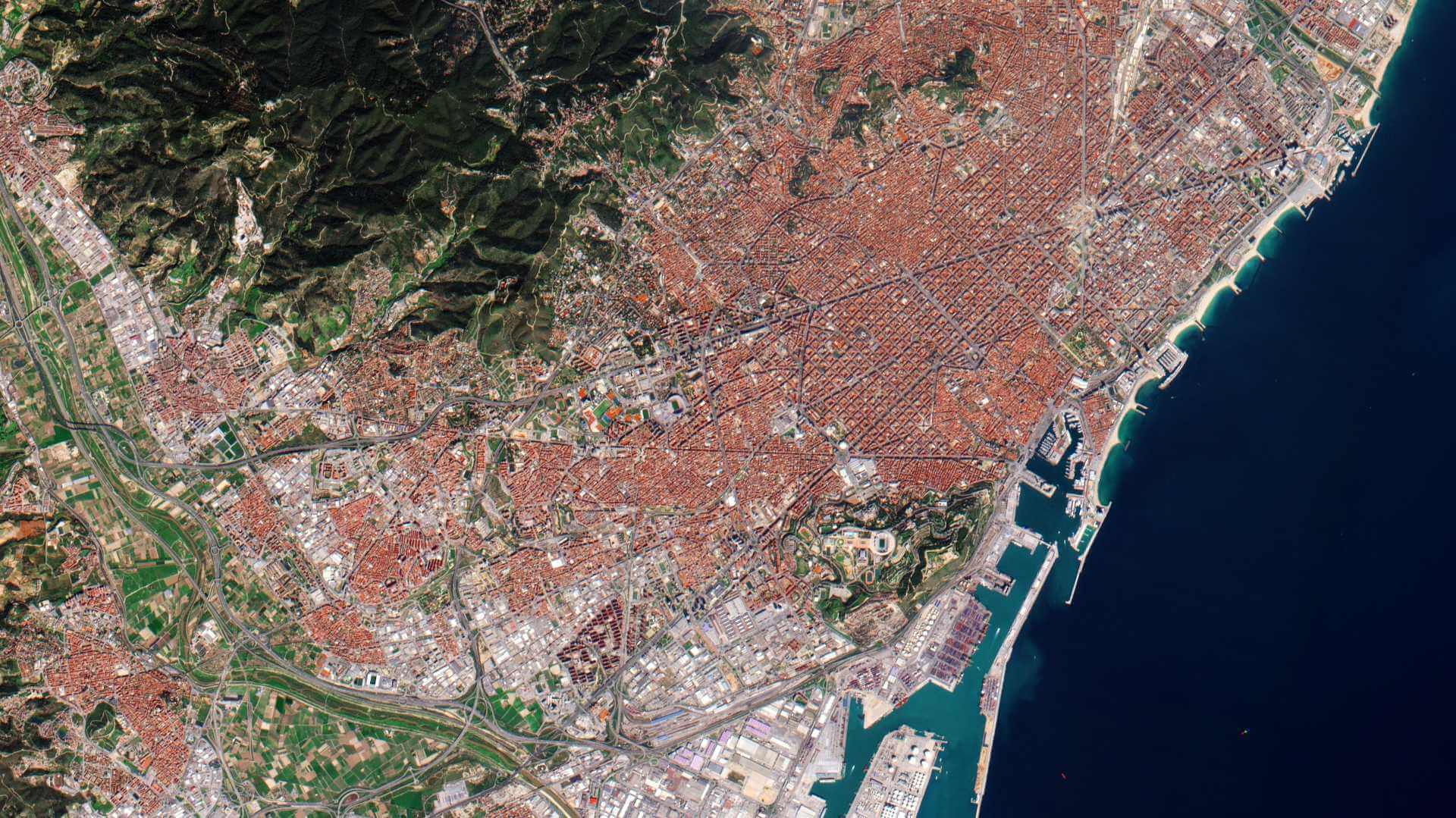
Featured
About ALOS-1

The Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS-1) was a Japanese Earth-imaging satellite from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that launched on 24 January 2006 and completed its operational phase on 12 May 2011 after failing due to a power anomaly.
ALOS-1 is part of ESA's Third Party Missions Programme, in which ESA has an agreement with JAXA to distribute data products from the mission.
ALOS-1 Objectives
The ALOS-1 mission objectives were:
- Providing its user community with data of sufficient resolution to be able to generate 1:25,000 scale maps
- Developing Digital Elevation Models and related geographic data products
- Performing regional observation to aid sustainable development goals
- Surveying natural resources
- Develop sensor and satellite technology for future Earth-observation missions
- Disaster monitoring around the world.
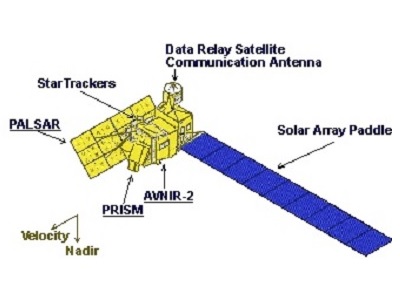
ALOS-1 Instruments
Find out more
Find out more

Find out more
The ALOS-1 instruments were capable of observing the entire surface of the Earth:
- Any place within two days
- Around the equator: about 60% of the area within one day
- At latitudes of 35°: about 70% of the area within one day
- At latitudes above 55°: any place every day (provided there is no cloud cover for the optical instruments)
Night-time observation modes: PALSAR (Note: AVNIR-2 and PALSAR are able to operate simultaneously).
PALSAR calibration is provided with PARC (Polarimetric Active Radar Calibrator) as well as by other means.
Non-scientific measuring instruments:
- AOCS (Attitude Orbit and Control System)
- RRA (RetroReflector Array)
- SST (Star Tracker)
ALOS-1 Data
DATA COLLECTIONS
Through the Online Dissemination server, ESA offers registered users access to the following data collections:

