Featured
About ERS

The ERS programme was composed of two missions, ERS-1 and ERS-2, which were launched into the same orbit in 1991 and 1995 respectively. The two spacecraft were designed as identical twins with one important difference – ERS-2 included an extra instrument (GOME) designed to monitor ozone levels in the atmosphere.
Due to the satellites' shared orbit, a tandem mission was implemented following the launch of ERS-2, whereby ERS-2 passed the same point on the ground one day later than ERS-1.
The 'ERS tandem mission' doubled the number of measurement points for the radar altimeter and, more importantly laid the basis for an accurate, three-dimensional digital map of Earth's land surfaces, which for some of Earth's regions would have been impossible.
Following nine years of excellent service, over three times its planned lifetime, the ERS-1 mission ended on 10 March 2000 due to a failure in the on board attitude control system.
Since its launch on 17 July 1991 ERS-1 made 45,000 orbits, acquiring more than 1.5 million individual Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) scenes.
ESA's venerable ERS-2 satellite followed its predecessor's example, greatly exceeding its three year life span with 16 years of successful operations. The satellite was safely taken out of service on 5 September 2011, due to low levels of remaining fuel. From when it was launched on 21 April 1995, ERS-2 made 85,000 orbits, travelling 3.5 billion km.
ERS Objectives
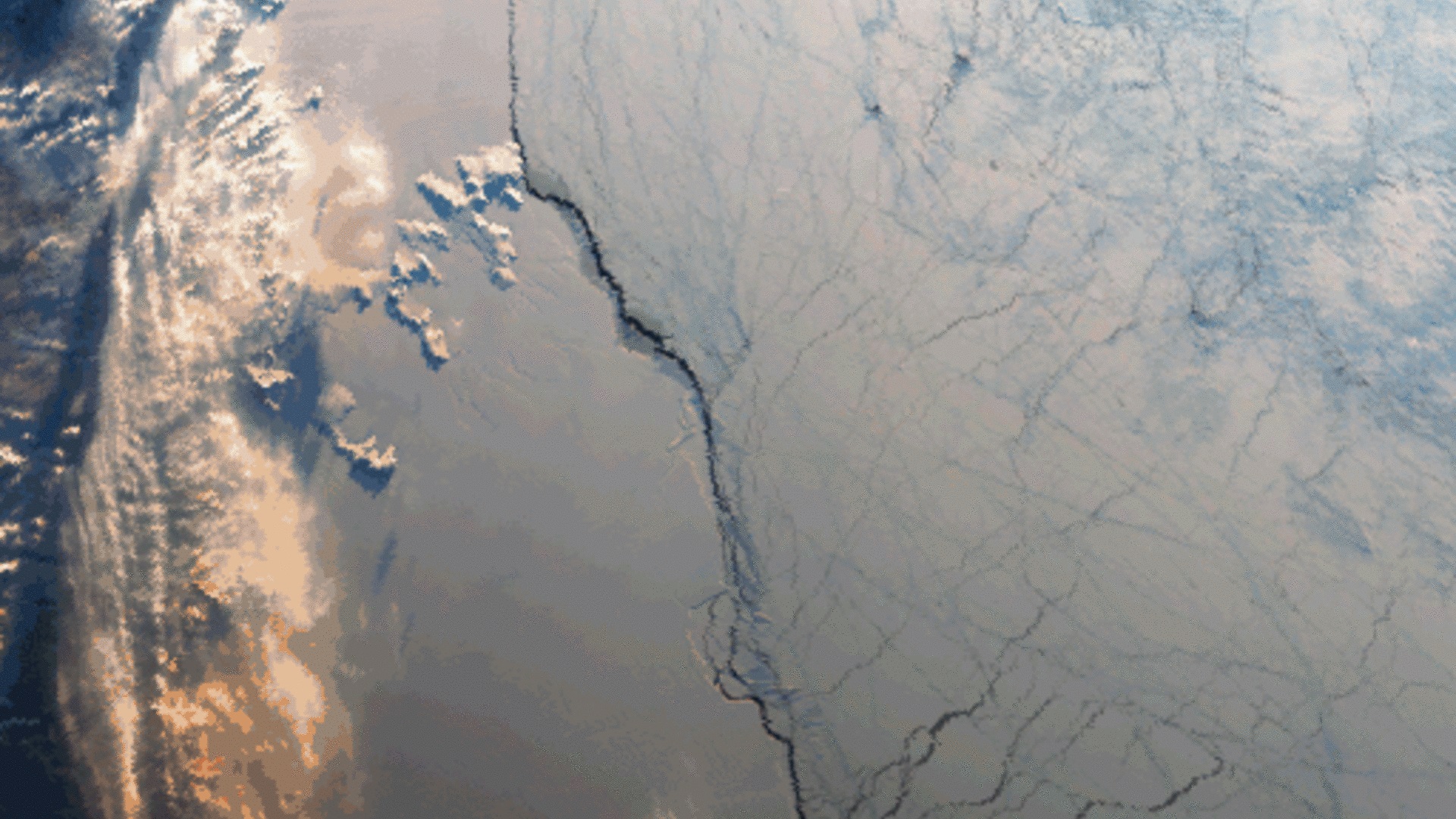
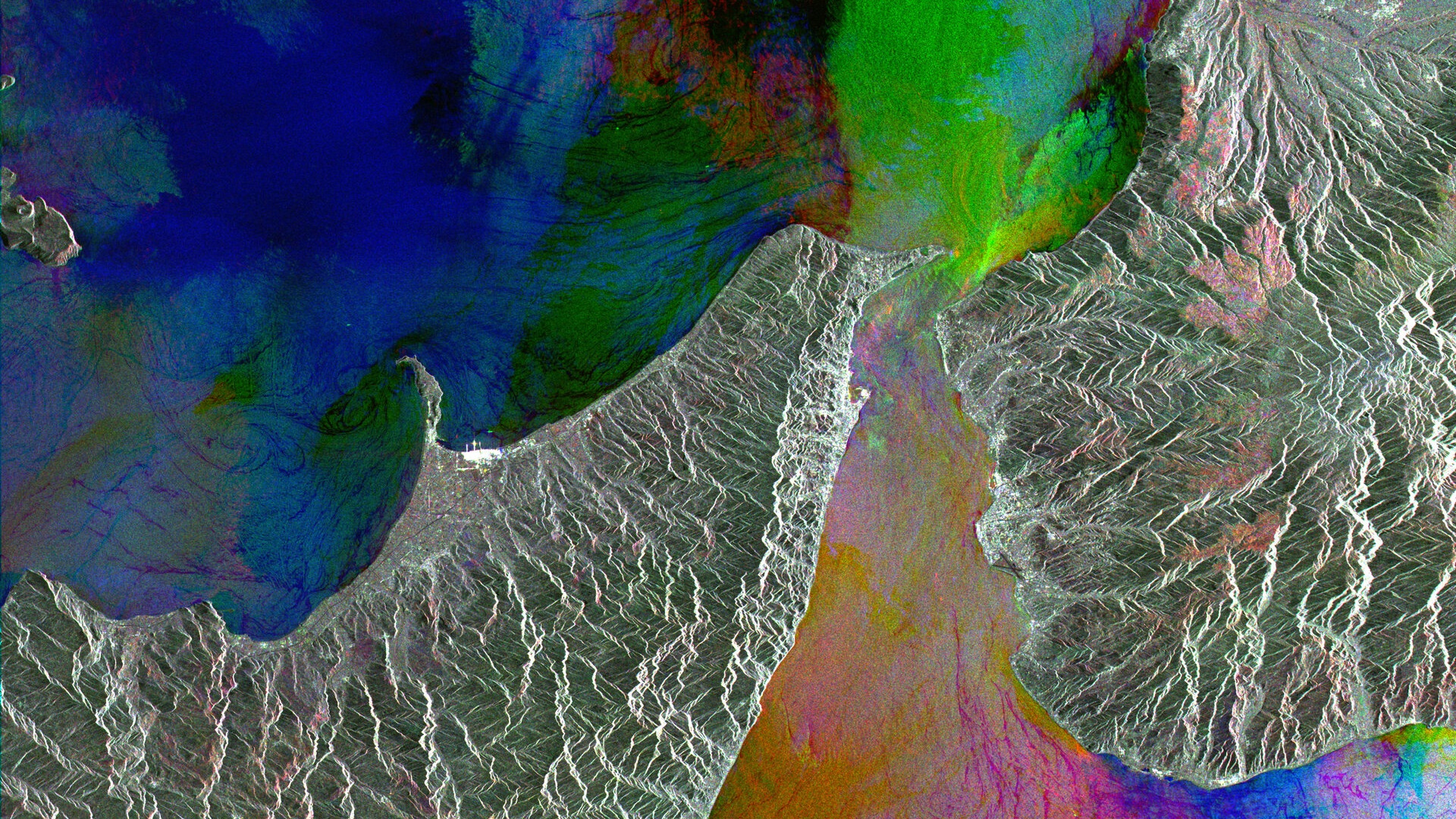
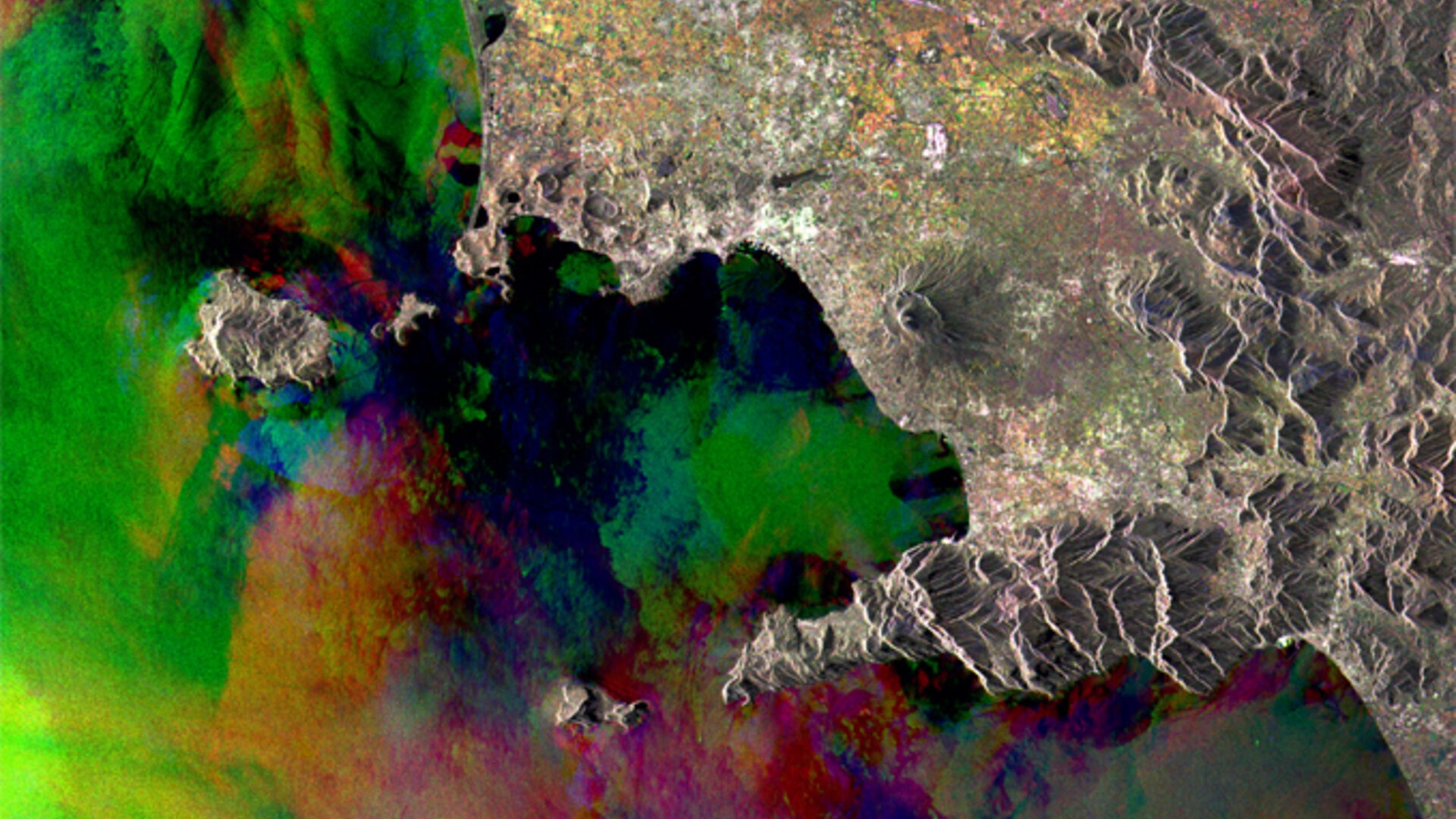
ERS was the first ESA programme in Earth observation to provide microwave spectrum-based environmental monitoring. The missions’ range of instruments were capable of monitoring the land, oceans, and atmosphere, and more specifically sea ice, geology, forestry, wave phenomena bathymetry, meteorological events and many more scientific fields.
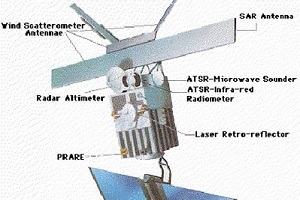
ERS Instruments
find out more

find out more


find out more

find out more

find out more

find out more

find out more