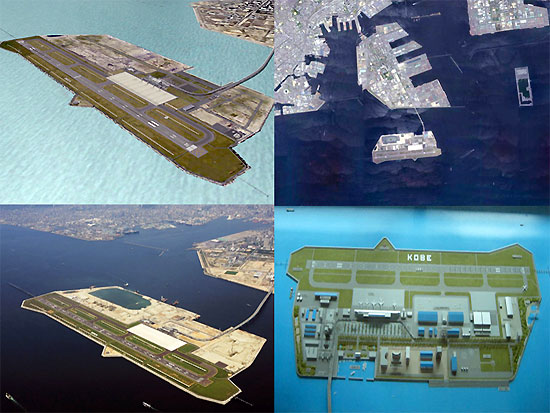
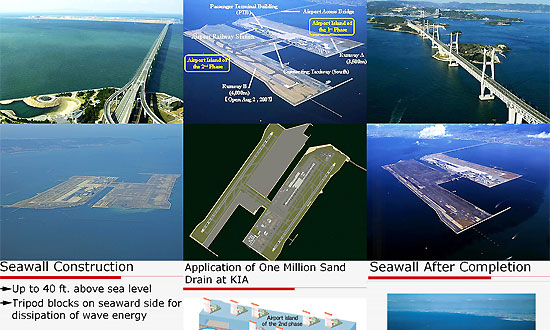
Kansai International Airport is located on an artificial island in the middle of Osaka Bay, 38 km southwest of Osaka Station, located within three municipalities, including Izumisano (north), Sennan (south) and Tajiri (central) in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. The airport is situated off the Honshu shore on a man-made island, 4 km long and 2.5 km wide. Engineers needed to overcome the extremely high risks of earthquakes and typhoons (with storm surges of up to 3 m) in the development. Construction started in 1987. The sea wall was finished in 1989 (made of rock and 48,000 tetrahedral concrete blocks). Three mountains were excavated for 21,000,000 m3 of landfill. 10,000 workers and 10 million work hours over three years, using eighty ships, were needed to complete the 30-metre layer of earth over the sea floor and inside the sea wall. In 1990, a three kilometre bridge was completed to connect the island to the mainland at Rinku Town, at a cost of $1 billion. Completion of the artificial island increased the area of Osaka Prefecture just enough to move it past Kagawa Prefecture in size (leaving Kagawa as the smallest by area in Japan).
It had been predicted that the island would sink 5.7 m by the most optimistic estimate as the weight of the material used for construction compressed the seabed silts. However, today the island has in fact sunk 8.2 m - much more than predicted. The project became the most expensive civil works project in modern history after twenty years of planning, three years of construction and several billion dollars of investment. Much of what was learned went into the successful artificial islands in silt deposits for New Kitakyushu Airport, Kobe Airport, and Chubu Centrair International Airport. The lessons of Kansai Airport were also applied in the construction of Hong Kong International Airport.
In 1991, the terminal construction commenced. To compensate for the sinking of the island, adjustable columns were designed to support the terminal building. These are extended by inserting thick metal plates at their bases. Government officials proposed reducing the length of the terminal to cut costs, but architect Renzo Piano insisted on keeping the terminal at its full planned length. The airport opened in 1994. On 17 January 1995, Japan was struck by the Kobe earthquake, the epicenter of which was about 20 km away from KIX and killed 6,434 people on Japan's main island of Honshu. Due to its earthquake engineering, the airport emerged unscathed, mostly due to the use of sliding joints. Even the glass in the windows remained intact. In 1998, the airport survived a typhoon with wind speeds of up to 200 km/h.
On 19 April 2001, the airport was one of ten structures given the "Civil Engineering Monument of the Millennium" award by the American Society of Civil Engineers. As of 2008, the total cost of Kansai Airport is $20 billion. This includes land reclamation, two runways, terminal and facilities. Most additional costs were initially due to the island sinking, expected due to the soft soils of Osaka Bay. After construction the rate of sinking was considered so severe that the airport was widely criticised as a geotechnical engineering disaster. The sink rate has since been reduced from 50 cm during 1994 to 7 cm in 2008.
|
ERS-1/2 SAR & Envisat ASAR_IMP Swath2 Animation |
This animation, composed of images taken by the ERS and Envisat satellites (Full Resolution), shows details of the area as it has changed over time. The animation features the phases of the different levels of airport construction starting from August 1993 to July 2009.
|
Radar multi-layer image of the area |
This multi-layer image is a merge between different images from the ERS-1/2 and Envisat satellites utilising the SAR/ASAR radar instruments. The image shows the different acquisitions in red (ERS-2), green (Envisat) and blue (ERS-1) taken as reference to highlight the development of the Airport and the bridge that connects it to the city.
|
Images used to create the multi-colour merge above |
|
Technical Information |
|
Product: |
SAR and ASAR - Level 1B (full resolution) |
|
Satellite: |
ERS-1/2 and Envisat |
|
Instrument: |
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) / ASAR (30 metre resolution) |
|
Acquisition date: |
19 Sep 2001, 27 Jul 2009, 08 Aug 1993 |
|
Merge layers: |
ERS-2, Envisat, ERS-1 |
|
Coverage: |
100 km along track |
Kobe Airport is located on an artificial island just off the coast of Kobe, 8 km south of Sannomiya Station, Japan. It primarily handles domestic flights with All Nippon Airways and Skymark Airlines, but can also accommodate international charter flights. The city government of Kobe first proposed an airport adjacent to Port Island in 1971. At the time, government planners were seeking alternatives to the heavily congested Osaka International Airport: the original Kobe Airport plan called for six runways more than 3,000 m in length on 2,700 acres for the facility.
|
Magnified view of Kobe Airport |
|
Landsat 5 and 7 animation - Kansai and Kobe structures |
This animation created with a series of images acquired with the Landsat 5 and 7 satellites, shows the phases of construction relative to the new airports with a different type of sensor (multispectral). Starting from April 1978 to June 2008, the user can see the progress of the development.
|
Images used to create the animation above |
|
Technical Information |
|
Product: |
TM / ETM - Level 1B (full resolution) |
|
Satellite: |
Landsat 5 and 7 |
|
Instrument: |
TM (30 metre resolution) |
|
Coverage: |
185 km x 185 km |
|
Band combination: |
7, 4, 2 (R-G-B) |
|
Technical Information |
|
Product: |
TM (full resolution) |
|
Satellite: |
Landsat 5 |
|
Instrument: |
TM (30 metre resolution) |
|
Coverage: |
185 km x 185 km |
|
Acquisition date: |
17 June 2008 |
|
Band combination: |
7, 4, 2 (R-G-B) |
Back to top