Featured
About Aeolus
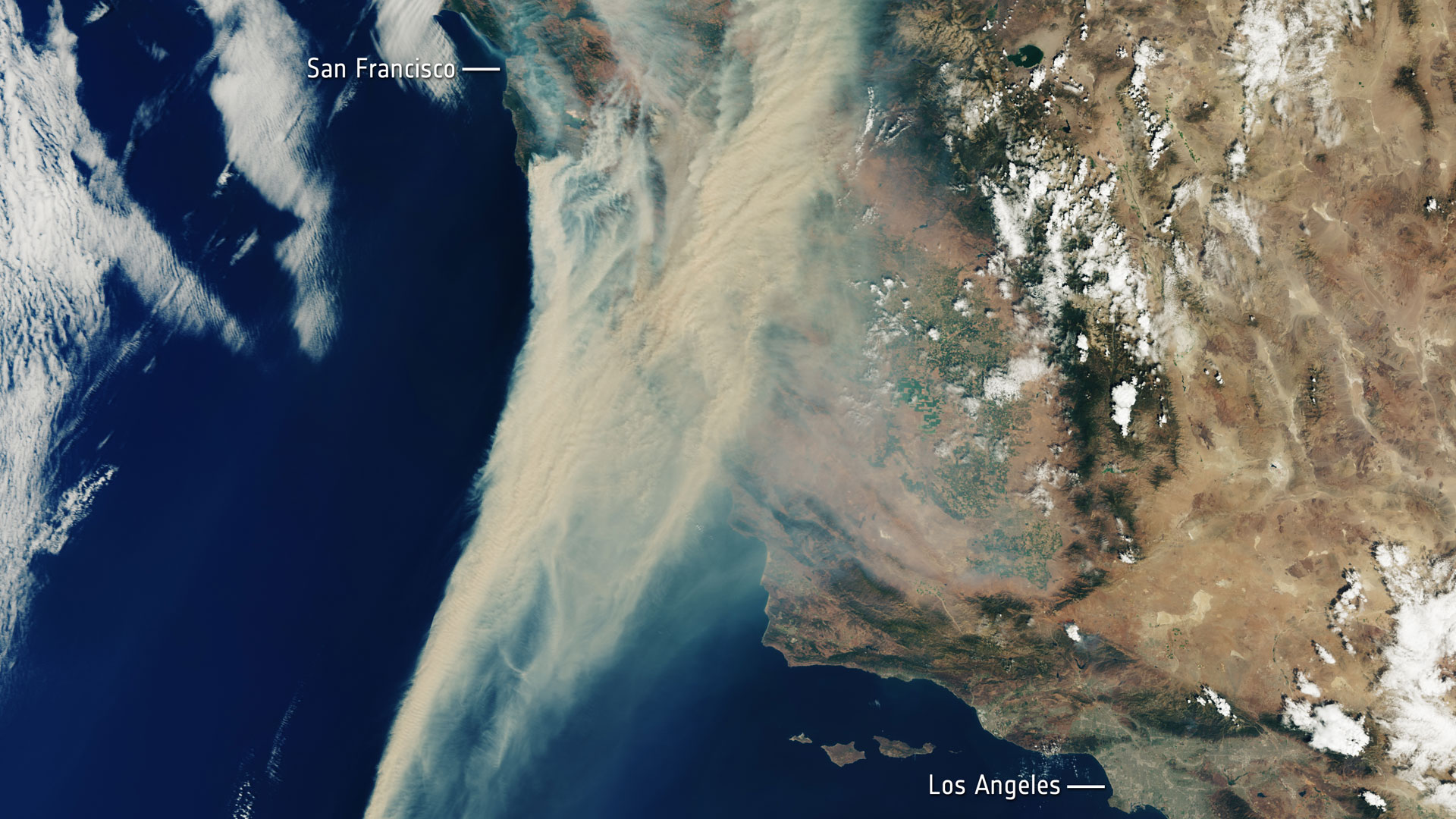
ESA's Earth Explorer, Aeolus, was launched into space on 22 August 2018 and was retired on 30 April 2023. Surpassing scientific expectations and exceeding its planned life in orbit, the mission has been hailed as one of ESA’s most successful.
It re-entered Earth’s atmosphere successfully on 28 July at around 19:00 UTC above Antarctica.
This new satellite type has provided novel global observations of wind profiles from the surface up to 30 km altitude.
Although there are several ways of measuring wind from a satellite, Aeolus utilised the active Doppler Wind Lidars (DWL) method. This is currently the only technology that can provide direct wind profile observations in clear air, inside thin clouds and aerosol layers and on top of thick clouds globally. In addition, a DWL provides information on cloud top heights and the vertical distribution of thin clouds and aerosol.
Aeolus's knowledge of Earth's wind fields has led to progress in atmospheric dynamics research and weather forecasting. Forecast impact experiments by a number of leading meteorological institutes across the world have shown that Aeolus observations led to an improvement of operational weather forecasting. The experiments showed that the impact is largest in the tropics, southern hemisphere, polar areas and in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere, where there are currently very few direct wind observations in the Global Observing System of the World Meteorological organization (WMO).
The provision of global wind profiles has also benefited climate research. Climate models are similar to weather models, but predict the evolution of the coupled Earth System (atmosphere, land, ocean and ice) on the scale of years rather than days. As for weather forecast models, the key atmospheric variables in climate models are wind, temperature, pressure and humidity. The Aeolus winds have been used to evaluate climate models, and for the improvement of modelling of the global atmospheric transport and cycling of energy, water, aerosols and chemicals.
Aeolus Objectives
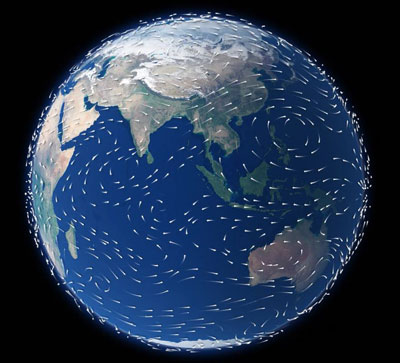
The Aeolus mission objectives were to provide accurate global measurements of winds from the surface up to 30 km.
The Aeolus mission has contributed to:
- Improving weather forecasts for society
- Understanding atmospheric dynamics
- Providing information on aerosols and clouds
- Filling the current major gap in the atmospheric observing system
- Understanding climate change
- Helping to track air pollution
- Tracking desert dust, smoke and volcanic ash
- Wind-energy management
- Paving the way for future wind lidar missions
Aeolus Instrument
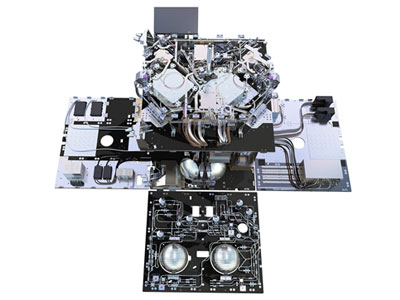
The Atmospheric Laser Doppler Instrument (ALADIN) was a Direct Detection Doppler Lidar operating in the ultra-violet spectral region (355 nm). The instrument generated and sent a series of short UV light pulses through its telescope into the Earth's atmosphere.
The UV light, which is invisible to the naked eye, was scattered by particles, ice crystals and cloud droplets (called Mie scattering) and air molecules (called Rayleigh scattering) along the path of the instrument's line-of-sight within its narrow field of view.




