- Spire
- Mission
- Spire Products Information
Spire Products Information
GNSS-PRO / STRATOS
GNSS-RO is a technique that provides unique temperature, pressure, and moisture vertical soundings through the atmosphere, similar to the type of data collected by a weather balloon. Rather than data being available only twice per day from specific sites, GNSS-RO utilizes Spire's satellite constellation to collect soundings 24/7 on a global basis and over remote regions like the oceans and the poles. In addition to being an important input for weather forecasting, GNSS-RO is also a climate quality measurement.
Spire is also seeking to enhance its measurements. Following the pioneering PAZ mission, Spire has designed, implemented, and operated a new Polarimetric-capable RO (PRO) payload. Unlike RO measurements, PRO measurements are shown to uniquely detect hydrometeors along the ray path, providing a novel method to characterize the presence of rain particles, snow, ice crystals, etc., with aims to augment weather forecasting.
GNSS-RO and PRO datasets are netCDF files provided at different levels, where the low levels are engineering outputs and high levels closer to scientific usage. For instance, proObs are Level 0 files containing raw open loop carrier phase measurements, while patmPrf are Level 2 files containing retrieved bending angles, dry refractivity, temperature. Level 1C polPhs data contain the novel polarimetric information, namely the differential phase difference (H-V) reflective of anisotropic hydrometeors.
A set of global historical data is accessible over 15 May 2023 to 30 November 2023, with additional periods available upon request.
GNSS Reflectometry (GNSS-R) / STRATOS
GNSS reflections captured by STRATOS are used to characterize the underlying surface for a variety of applications such as soil moisture, sea ice classification, etc. There are two types of GNSS-R: Near-Nadir (NN) and Grazing Angle (GA).
The NN GNSS-R tracks are collected by several satellites. Similarly to PRO datasets, several levels of netCDF files are available. Level 1 represent along-track calibrated and normalized bistatic radar cross-sections. Currently, Level 2 products come in two forms: 1) land retrievals with a focus on soil moisture and 2) ocean winds and mean square slopes.
The GA GNSS-R tracks are collected opportunistically by RO satellites with a focus on the polar areas and the northern hemisphere land areas. The Level 1 products contain reflectivity, SNR, phase-delay, and other related observables, along with receiver and transmitter positions. The two Level 2 products focus on water and sea ice classification, along with phase-delay altimetry.
Data are accessible over 24 January 2024 to 25 July 2024, with additional periods available upon request.
AIS / Maritime 2.0
All large ocean-going vessels and passenger vessels are required by the International Maritime Organization to install an AIS transponder and broadcast information about their location and surroundings. Spire captures and decrypts the vessel transponder signal from its satellite constellation as well as land-based receivers. The data is cleaned, attached to specific vessel identifiers, and combined with other vessel-specific information to create a global database of ocean-going vessels that is updated on 6-minute intervals.
Data Statistics
- AIS devices detected: 600,000+
- Active vessels per day: 250,000+
- Coverage: Global
- Data update interval: average 6 minutes
ADS-B / AirSafe
Commercial, military, business, and personal aircraft are facing new regulations that require the installation of ADS-B transponders by 2020. Most commercial and business jets are already equipped and regularly send information about their location and speed that Spire captures from its satellite constellation. Spire is at the forefront of space-based ADS-B collection and can track over the oceans, poles, and remote areas where ground-based receivers cannot be installed.
Total Electron Content / STRATOS
When the GNSS receiver on-board a Spire satellite is powered on, it continuously tracks multiple dual-frequency GNSS satellite signals simultaneously from the POD antenna. These signals are primarily used for the purpose of precise orbit determination, which is necessary for neutral atmospheric radio occultation inversion. However, the pseudorange and carrier phase measurements measured by the receiver are also used to derive an estimate of the ionospheric total electron content (TEC) along the line-of-sight to each GNSS satellite. During post-processing, the TEC is computed for each signal "arc" (i.e. the period when the Spire receiver is continuously tracking a particular GNSS satellite) by forming a linear combination of phase measurements from dual GNSS frequencies. The phase TEC measurements are then "leveled" to the analogous combination of the pseudorange measurements for a more accurate measurement. Receiver and transmitter differential code biases are removed when possible.
The computed TEC values are stored in standard NetCDF format along with ancillary information including the transmitter and receiver positions. These data sets are packed in a NetCDF format, following conventions derived from data products created by CDAAC.
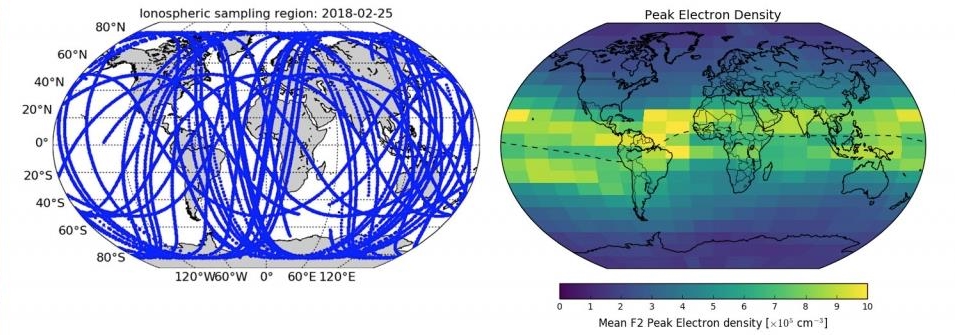
Ionospheric Scintillation Indices / STRATOS
Scintillation indices are indicators for ionospheric turbulence and are subdivided into two classifications: amplitude scintillation (S4), and phase scintillation (σɸ). Both provide indicators for "space weather" in the upper atmosphere. For example, large S4 values from a GNSS link may indicate ionospheric "storms" consisting of electron density gradients (e.g., Equatorial Spread F). This could lead to loss-of-lock on GNSS receivers, jeopardizing a receiver's ability to provide robust and accurate Position, Navigation, and Timing (PNT). Continuous monitoring of scintillation indices is key for understanding GNSS link health, and is a first step toward predicting potential GNSS regional outages.
Spire's CubeSats feature an advanced scintillation monitoring capability and can measure both amplitude and phase scintillation (S4 and σɸ). Combined with both a large constellation (~100 CubeSats) and diverse orbital planes, Spire's constellation is prepared to contribute critical ionospheric data, particularly over Equatorial regions.
These data sets are packed in a NetCDF format, following conventions derived from data products created by CDAAC.
Magnetometer Data
Magnetometer data is collected continuously on Spire spacecraft as part of our Attitude Control and Determination (ADCS) system. The sensor used is based on magneto-inductive technology to deliver high-performance resolution and repeatability with high gain, high sample rates, low hysteresis, and no need for temperature calibration.
Spire can provide the magnetic field vector (x, y, z + unix timestamp) Unit: nT. The time resolutions is 4 Hz or 0.1 Hz.