- MetOp
- Mission
- MetOp Overview
MetOp Overview
Mission Background

The MetOp satellites were originally to be part of a much larger satellite concept called the Polar-Orbit Earth Observation Mission (POEM), which was to have been the successor to ERS-1 and ERS-2. The payload was to cover research aspects of environment as well as provide operational meteorological data. Instead, in 1992, the ESA Ministerial Council decided to split the POEM mission into two satellite concepts and hence the Environmental Satellite (Envisat) and MetOp were born.
The development and procurement of the three MetOp satellites is a joint undertaking by ESA and EUMETSAT and forms the space segment of EUMETSAT's Polar System (EPS). In addition to the space segment, the EPS comprises the ground segment, the launch and various infrastructure elements.
EPS is Europe's first polar orbiting operational meteorological satellite system and is the European contribution to the Initial Joint Polar Satellite System (IJPS). This was a result of a cooperative effort between NOAA and EUMETSAT whereby MetOp flies in the morning orbit, that is it passes over the Equator at the same local time each orbit (09.30 descending node) and the NOAA satellite flies in the afternoon orbit.
Satellite Design
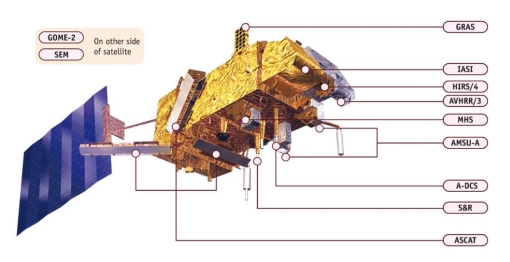
On board Sensors
- A-DCS (Advanced Data Collection System)
- AMSU-A1 and AMSU-A2 (Advanced Microwave Sounding Units)
- ASCAT (Advanced Scatterometer)
- AVHRR/3 (Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer)
- GOME-2 (Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment-2)
- GRAS (Global Navigation Satellite System Receiver for Atmospheric Sounding)
- HIRS/4 (High-resolution Infrared Radiation Sounder)
- IASI (Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer)
- MHS (Microwave Humidity Sounder)
- SARP-3 (Search and Rescue Processor)
- SARR (Search and Rescue Repeater) & SEM-2 (Space Environment Monitor)
The MetOp series, developed by a consortium of European companies led by the main contractor EADS-Astrium (now Airbus DS), France, builds on the heritage gained from a successful series of European satellites, including the French space agency (CNES) SPOT and ESA’s ERS and Envisat.
The satellite consists and two modules: the Payload Module (PLM) and the Service Module (SVM), and a large solar array. It includes advanced versions of the widely used scatterometer and ozone-monitoring instruments that flew on the ERS-2 satellite. The SVM provides the main satellite support functions, such as command and control, communications with the ground, power and orbit control and propulsion. The PLM accommodates the whole suite of instruments and associated support equipment.
MetOp carries a set of 'heritage' instruments, provided by (NOAA) and CNES, and a new generation of European instruments offering precise sensing capabilities to both meteorologists and climatologists.
The new instruments provide high-accuracy vertical profiles of atmospheric temperature and humidity as well as measurements of wind speed and direction over the ocean. Atmospheric trace gases, notably ozone, are also measured.
Together with the instruments, the satellite weighs 4.1 tonnes and measures 17.6 m x 6.6 m x 5.2 m when in orbit, making it the second largest European Earth observation satellite, after Envisat.
Technical Specifications
- Dimensions: 6.2 x 3.4 x 3.4 m (under the launcher fairing)
- 17.6x6.5x5.2 metres (deployed in orbit)
- 4083 Kg at launch, including 314 Kg of fuel
Resolution
- AMSU-A: 48 km
- ASCAT: <50 km
- AVHRR: 1 km
- GOME-2: 80 x 40 km or 160 x 40 km
- HIRS/4: 10 km
- IASI: 12 km
Swath Width
- AMSU-A: 2074 km
- ASCAT: 500 km
- AVHRR: 2000 km
- GOME-2: 960 or 1920 km
- HIRS/4: 2160 km
- IASI: 2112 km
- MHS: 1920 km
Mission Operations
- Orbit Polar, Sun-synchronous orbit
- Repeat Cycle 29 days
- Altitude Approximately 817 km
A number of ground facilities support the operations of the MetOp satellites.
Mission control is conducted at EUMETSAT in Darmstadt, Germany
Launch and early orbit phase is carried out via ESA's European Satellite Operations Centre in Darmstadt.
Data is downloaded to EUMETSAT Polar System stations in Svalbard, Norway and U.S. McMurdo in Antarctica.
Data is processed at EUMETSAT.