- News
- Ground-based campaigns support...
Ground-based campaigns support NO2 monitoring in Po Valley
27 Jan 2022
The Po Valley in Italy is one of the most polluted regions in Europe. High NO2 concentrations often occur due to industrial and urban activities and the topography of the Po River basin, where the Alps and Apennines limit the dispersal of pollutants.
Ground-based instruments are being used to acquire data over Po Valley, which will help calibrate and validate satellite data of the region and fill a gap in measurements that help accurately monitor pollution levels.
The Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS) technique is used to monitor NO2 abundance and therefore ground-based Multi-AXis (MAX) DOAS instruments are located in the most polluted areas of Europe. However, until last year, an instrument compliant to the Fiducial Reference Measurements for Ground-Based DOAS (FRM4DOAS) standards, was not present in the Po Valley.
In the frame of the IDEAS-QA4EO contract, the Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate of the Italian National Research Council (ISAC-CNR) and Serco aim to fill this gap through use of the ground-based custom instrument TropoGAS (Tropospheric Gas Analyser Spectrometer), installed on the roof of the ISAC-CNR institute in Bologna.
An inter-comparison campaign was performed at ISAC-CNR in May 2021. NO2 vertical column densities (VCDs) retrieved from TropoGAS zenith-sky measurements were compared with Copernicus Sentinel-5P TROPOMI data, observing a bias of +6%. The lowest points of the NO2 retrieved profiles were compared with in-situ data measured by an Aerosol, Clouds and Trace Gases Research Infrastructure (ACTRIS) compliant NOX chemiluminescence analyser, revealing good agreement.
In the frame of an Italian-funded programme, ISAC-CNR acquired a new ground-based spectrometer, called SkySpec-2D. Produced by Airyx, SkySpec-2D is fully FRM4DOAS compliant, and is now used for IDEAS-QA4EO activities.
An inter-comparison campaign between TropoGAS and SkySpec-2D was performed in Bologna in August 2021 (Figure 1). A generally good agreement between the two instruments was observed, and though the design of TropoGAS is old and a few components are ageing, it was still able to acquire accurate measurements.

SkySpec-2D was then used in a measurement campaign at the BAQUNIN supersite from 7 to 21 September 2021 (Figure 2).

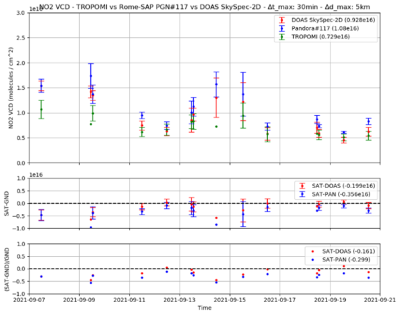
Figure 3: Analysis of SkySpec-2D (red dots) and Pandora#117 (blue dots) NO2 VCDs with respect to the Sentinel-5P TROPOMI NO2 products (green dots). The co-location criteria: Δd_max= 5 km and Δt_max = ±30 minutes. The absolute (mid panel) and the percentage relative (lower panel) differences between the ground-based and satellite instruments are reported.
Today, the Po Valley has two MAX-DOAS instruments installed; SkySpec-2D at the rural site of San Pietro Capofiume and TropoGAS in Bologna at ISAC-CNR. Both instruments routinely monitor NO2 levels in the valley, helping to gather data on this region and continue to provide calibration and validation for Sentinel-5P TROPOMI.