- Biomass
- Mission
- Biomass Overview
Mission Overview
Biomass Infographic
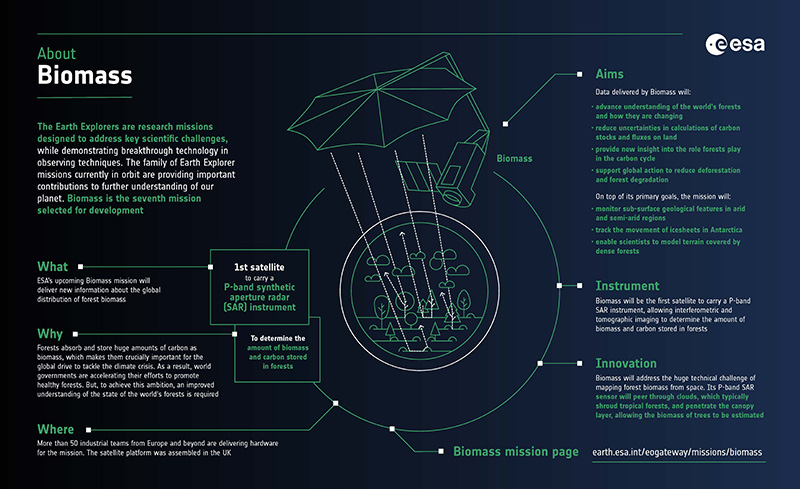
Learn about ESA's upcoming Biomass mission, which is dedicated to gathering information about the global distribution of forest biomass, in this infographic.
Satellite Design
The Biomass mission will consist of a single LEO (Low Earth Orbit) satellite platform carrying the SAR instrument. ESA's forest mission is being designed to provide P-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) measurements to determine the amount of biomass and carbon stored in forests.
The Biomass SAR operates in a stripmap mode with a swath illuminated by a single antenna beam, i.e. an imaging configuration similar to that of the ERS-1/2 SAR. Global coverage is obtained by the interleaved stripmap operations among three complementary swaths.

The antenna aboard Biomass is based on a large deployable reflector (12 m circular projected aperture) with an offset feed array and a single-beam. The satellite configuration is strongly constrained by the accommodation of the very large reflector antenna inside the Vega launcher. This large antenna must be folded for launch and deployed in orbit to form a stable aperture throughout the mission's life.
Exploiting the unique sensitivity of P-band SAR together with advanced retrieval methods, maps of forest biomass and forest height at a resolution of 200 m will be generated. In addition, the mission will have an experimental 'tomographic' phase during its first year of operations to provide 3D views of forests. This is necessary, as the global mass of trees is not obtainable by ground measurement techniques.
Satellite specifications:
- Dimensions: three-axes stabilised platform 10 m high, 12 m wide and 20 m long (including large reflector)
- Mass: 1170 kg (including 67 kg fuel)
- Instrument: synthetic aperture radar operating at P-band (435 MHz); fully polarimetric
- Power: 1.5 kW deployable solar array with 6.8 m2 triple junction GaAs cells; 144 Ah Li-ion battery
- Mission life: Five years (including a tomographic phase of one year)
Mission Operations
Biomass will operate in a Sun-synchronous near circular dawn-dusk orbit (LTAN of 06:00 hours) at an altitude of 666 km, depending on the different mission phases.
The orbit is designed to enable repeat pass interferometric acquisitions throughout the mission's life and to minimise the impact of ionospheric disturbances. The baseline observation principle is based on double-baseline interferometric acquisitions.
Biomass will be supported through a number of ground facilities:
- Mission control: ESA's European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany
- Communication links: ESA's ground station in Kiruna, Sweden, via X-band downlink (310/520* Mbit/s) for science data; via S-band uplink (64 kbit/s) and downlink (128 kbit/s) for tracking, telemetry and command
- Data: processing at ESA's Centre for Earth Observation (ESRIN) in Frascati, Italy
- Project and commissioning: managed at ESA's European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) in Noordwijk, Netherlands